Describe the Basic Structure of a Cell
The general structure is explained by the separation of individual substances based on their attraction or repulsion of water. It is considered to be the brain of the cell.
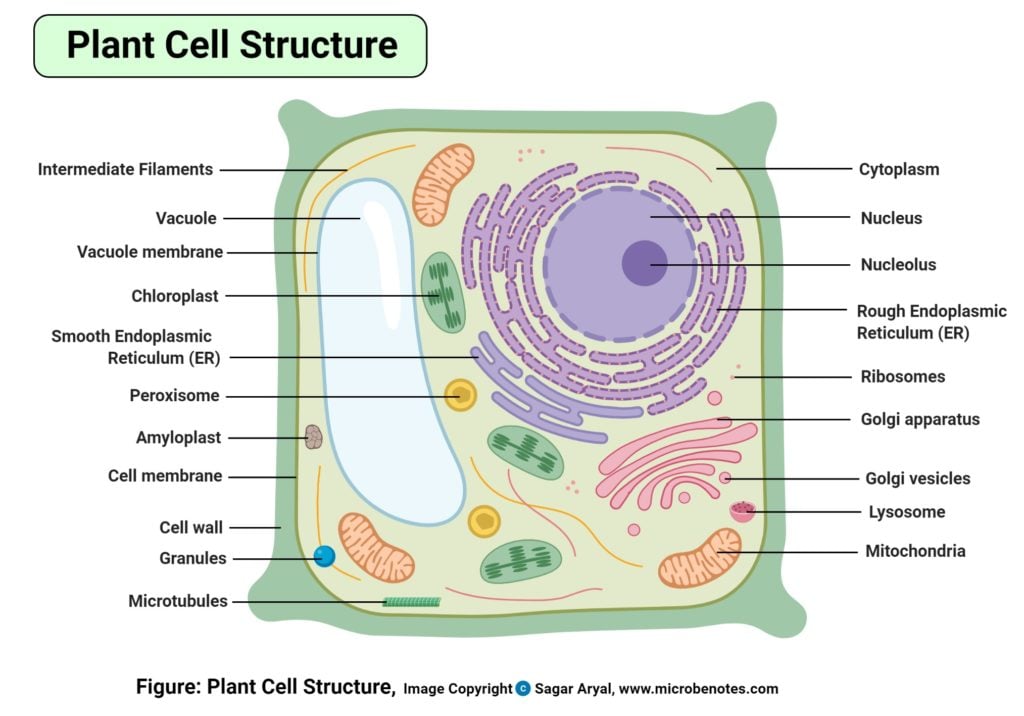
25 Major Difference Between Plant Cell And Animal Cell
Describe the structure of cell membranes.
. The cytoplasm is the gel-like. It is a jelly-like fluid that fills up the part of the cell between the cell membrane and the nucleus. The cell membrane is only one component of a cell.
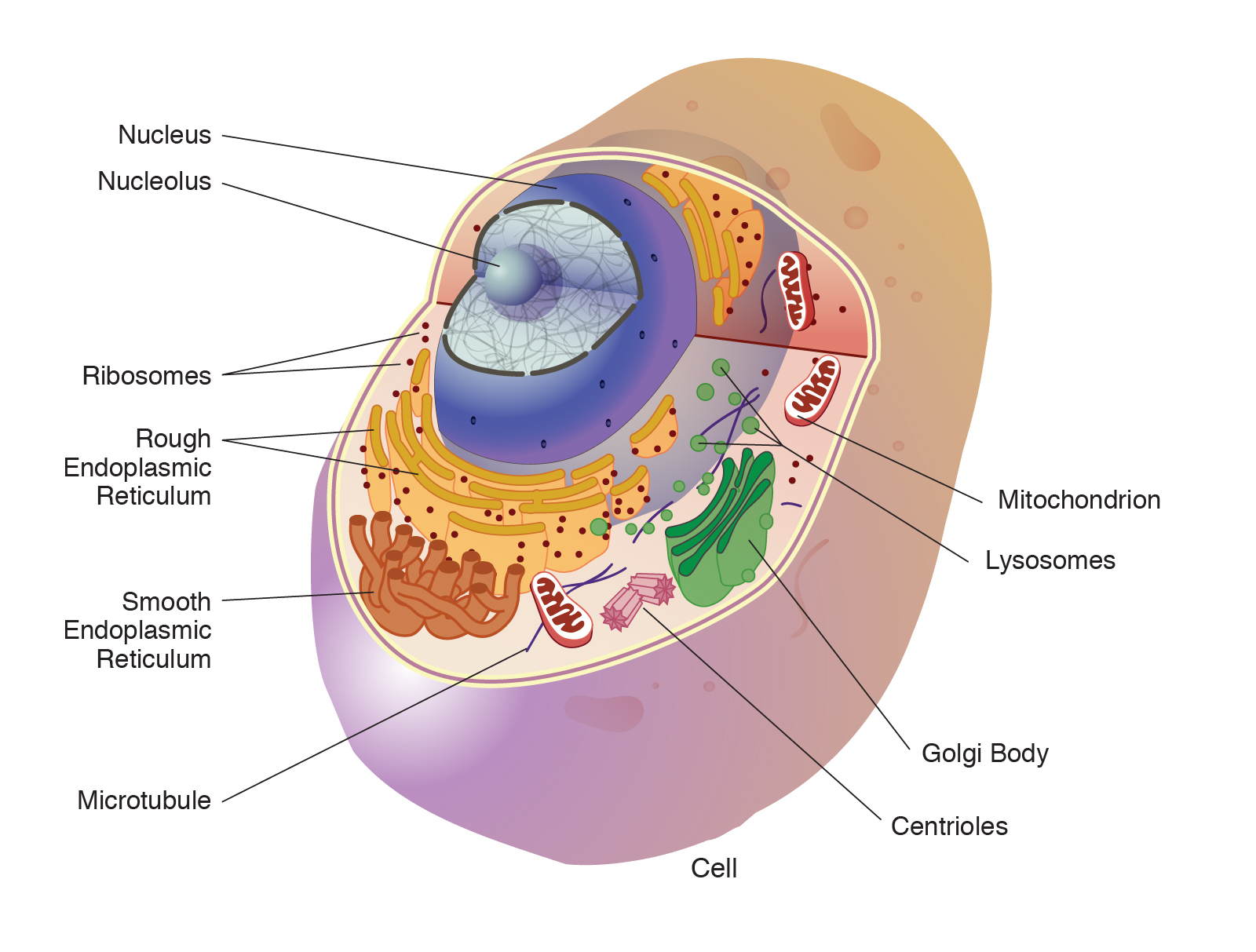
A cell having following Structure and Function of cell Organelles. Cell membrane cellular organelles cytoplasm and nucleus. It is a porous membrane through which selected substances can enter or leave the cell.
The following cell structures can also be found in a typical animal eukaryotic cell. Lets begin our study of the cell by investigating the basic anatomy of an animal cell. The cell structure is defined by the cell membrane the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
The cell membrane separates the material. A cell membrane which surrounds and protects the cell. The cytoplasm which is the watery interior of the cell which contains ions proteins and organelles.
Identify components of the cell membrane including phospholipids cholesterol proteins and carbohydrates. Major Cell organelles are as follows 1Cell Membrane-Cell membrane enclose the cell and regulates the in and out flow of substance. A microscope is required to study cell structure.
T he cell membrane separates the material outside the cell extracellular from the material inside the cell intracellular. These components include- cell wall cell membrane cytoplasm nucleus and cell organelles. All cells are made of three main structures.
Every cell in the body is enclosed by a cell Plasma membrane. Within the cytoplasm lie intricate arrangements of fine fibers and hundreds or even thousands of miniscule but distinct structures called organelles. Cytoskeletal elements are usually absent.
These cells reproduce both asexually and sexually. Cell Membrane the semi-permeable structure that surrounds the cell and keeps all of the cells organelles from exploding everywhere. Cells exclude some substances take in others and excrete still others all in controlled quantities.
A cell is the smallest unit of life and its structure helps it to work as the basic building block of biology. Although we defined the cell as the most basic unit of life it is structurally and functionally complex Figure 221. Cilia and Flagellaaid in cellular locomotion.
Several organelles are embedded in the cytoplasm. Up to 24 cash back Basic Cell Structure. No membrane-bound organelles and no nucleus.
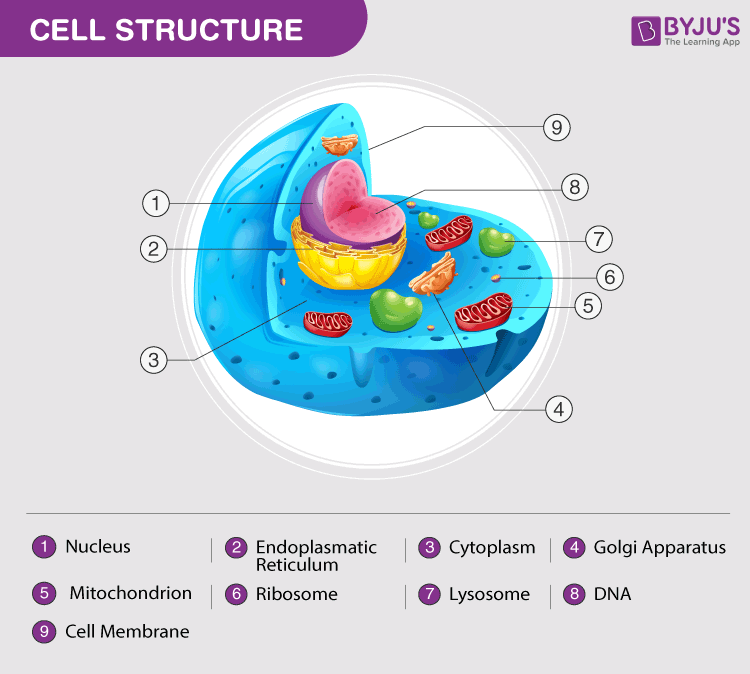
Each cell consists of three components shown in the image above. Cell membranes are at their most basic composed of a phospholipid bilayer with some surface proteins embedded around the surface. Centrioleshelp to organize the assembly of microtubules.
Cell Structure Cell membrane. It maintains the integrity of a cell and controls passage of materials into and out of the cell. The cell membrane is semipermeable and flexible.
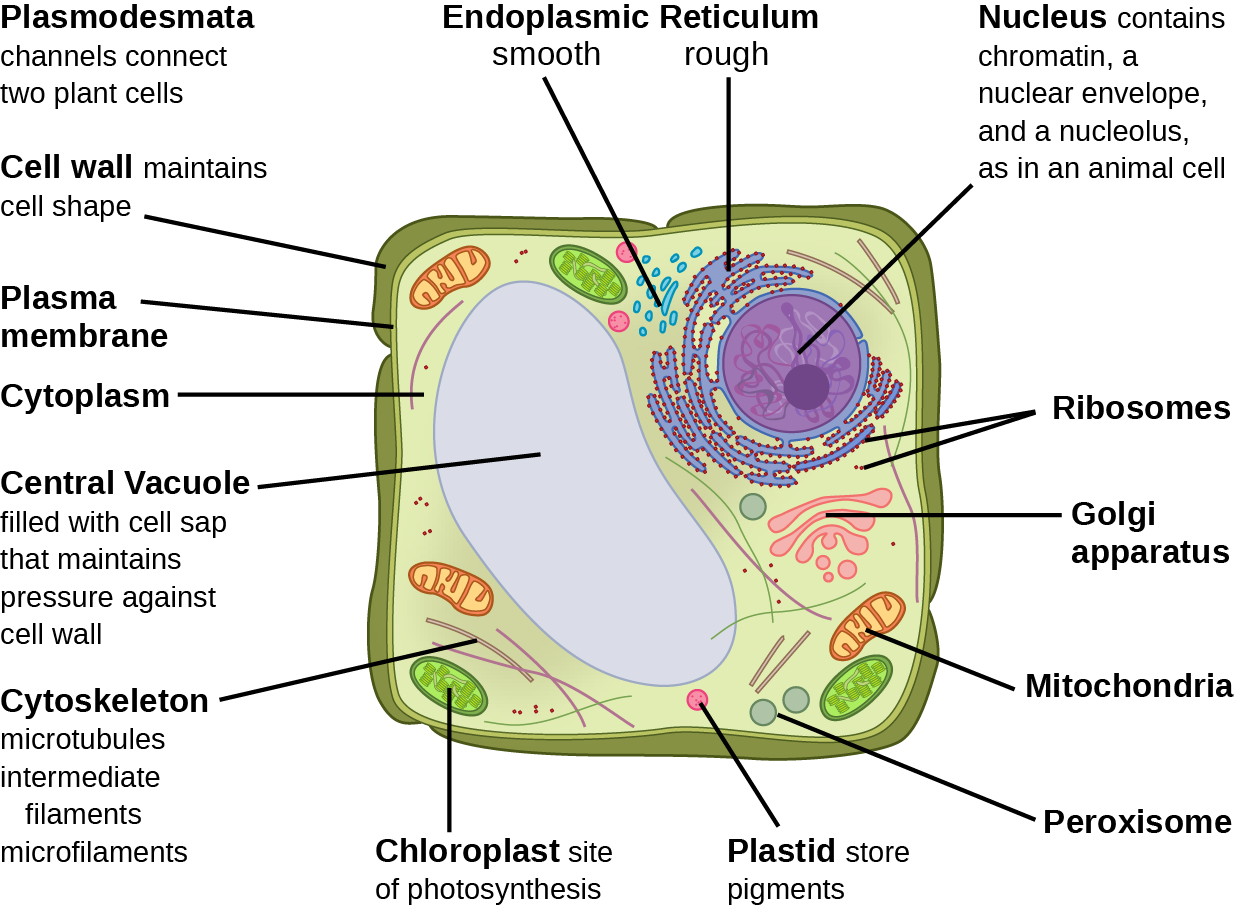
Describe the basic structure of a plant cell wall. A nerve cell neuron consists of a large cell body and nerve fibersone elongated extension axon for sending impulses and usually many branches dendrites for receiving impulses. The human body is made up of roughly 10 trillion cells each held together by a cell membrane.
The basic components of a human cell are the cell membrane the cytoplasm the nuclear membrane and the nucleus. In some cases the capsid is surrounded by an envelope which is usually a bilayer of glycoprotein and lipoproteins. The nucleus formed by a nuclear membrane around a fluid nucleoplasm is the control center of.
Cell membranecytoplasm and nucleus. Within each of these parts are smaller structures such as the organelles which have specialized functions within the cell. Nucleuscell membrane and cytoplasm are the basic structure of cell.
A cell can be thought of as a mini-organism consisting of tiny organs called organelles. The cells are comparatively larger in size 10-100 μm. The plant cell wall is an elaborate extracellular matrix that encloses each cell in a plant.
The membrane is typically composed of two layers a bilayer of phospholipids which form the basic structure. The impulses from the axon cross a synapse the junction between two nerve cells to the dendrite of another cell. Cells are the basic building blocks of all.
A basic structure of a cell consists of three parts. The organelles are structural and functional units constructed from several macromolecules bonded together. Eukaryotes are sophisticated cells with a well defined nucleus and cell organelles.
The cell membrane is also called plasma membrane. It is present in all the plant cells. Plasma membranes contain phospholipids cholesterol proteins and carbohydrates that are arrayed in regular repeating rows to form a highly plastic surface for the cell.
A cells plasma membrane defines the cell outlines its borders and determines the nature of its interaction with its environment. All living things plants animals fungi bacteria etc are made of cells. These structures are the cell membrane the cytoplasm and the nucleus.
Read on to explore more insights on cell structure and function. Endoplasmic Reticulumsynthesizes carbohydrates and lipids. Unicellular to multicellular in nature and evolved 1 billion years ago.
Start studying Basic Structure of a Cell. The cell structure comprises individual components with specific functions essential to carry out lifes processes. The cell function is to keep all of the functions of the body performing as intended.
Describe the basic structure of the cell. Learn vocabulary terms and more with flashcards games and other study tools. Scientist Robert Hook First studied the cell structure in the year 1665 using a self designed microscope.
The basic structure of all viruses includes nucleic acid either DNA Deoxyribonucleic Acid or RNA Ribonucleic Acid called a genome which is enveloped by a protein coat called a capsid. This includes keeping toxins out of the body help to break down waste make. The cell membrane supports and protects the cell.
Describe the basic structure of a nerve.

Parts Of A Human Cell Diagram Of The Human Cell Illustrating The Different Parts Of The Cell Human Cell Diagram Cell Diagram Human Cell Structure

Mike Thinks What Is Going On Inside That Cell Human Cell Diagram Cell Diagram Human Cell Structure
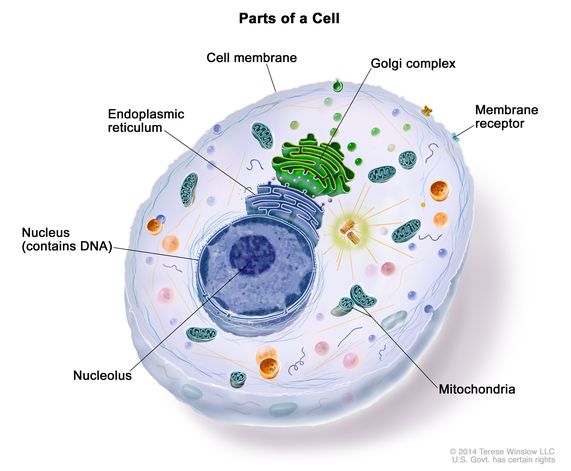
Definition Of Cell Nci Dictionary Of Cancer Terms National Cancer Institute
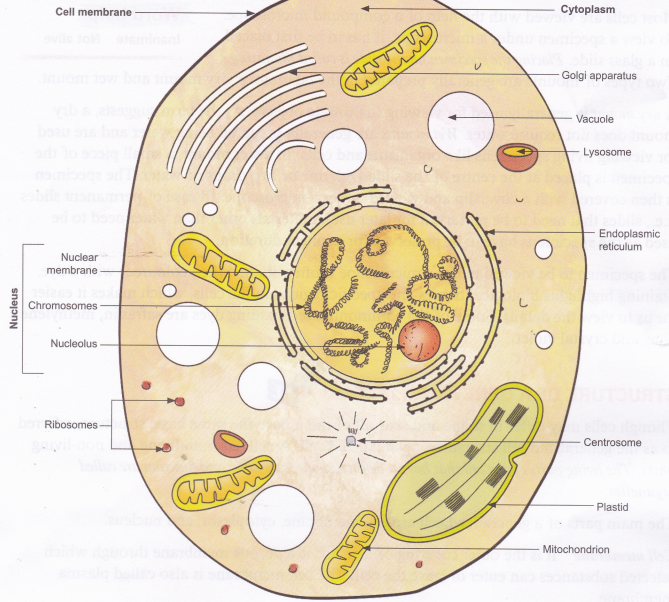
Describe The Structure Of A Generalized Cell A Plus Topper

Cell Definition Types Functions Diagram Division Theory Facts Britannica
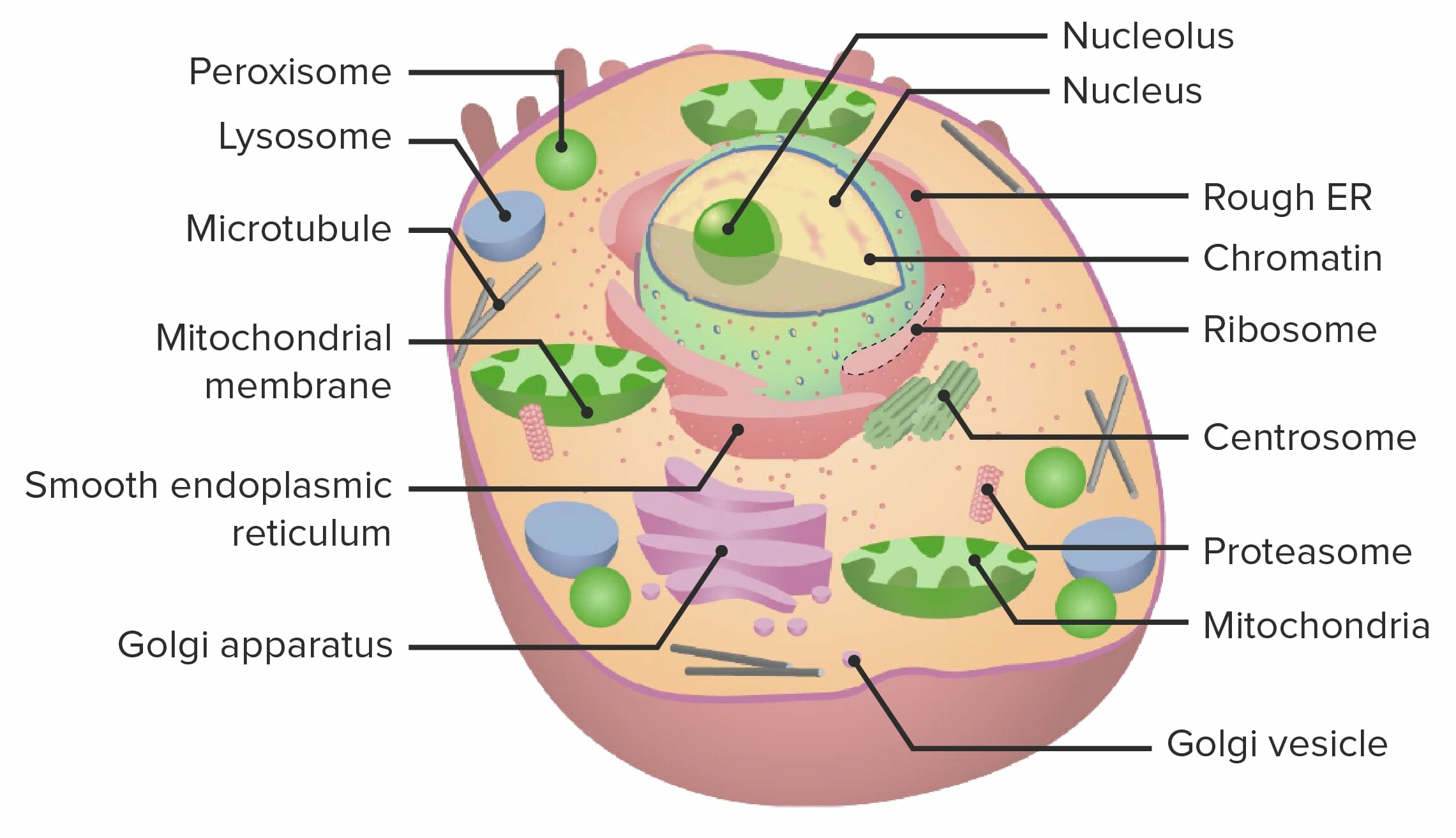
The Cell Organelles Concise Medical Knowledge

Eukaryotic Cell Structure Eukaryotic Cell Cell Biology Cell Parts

Plant Cell The Definitive Guide Biology Dictionary

Cell Definition Types Functions Diagram Division Theory Facts Britannica
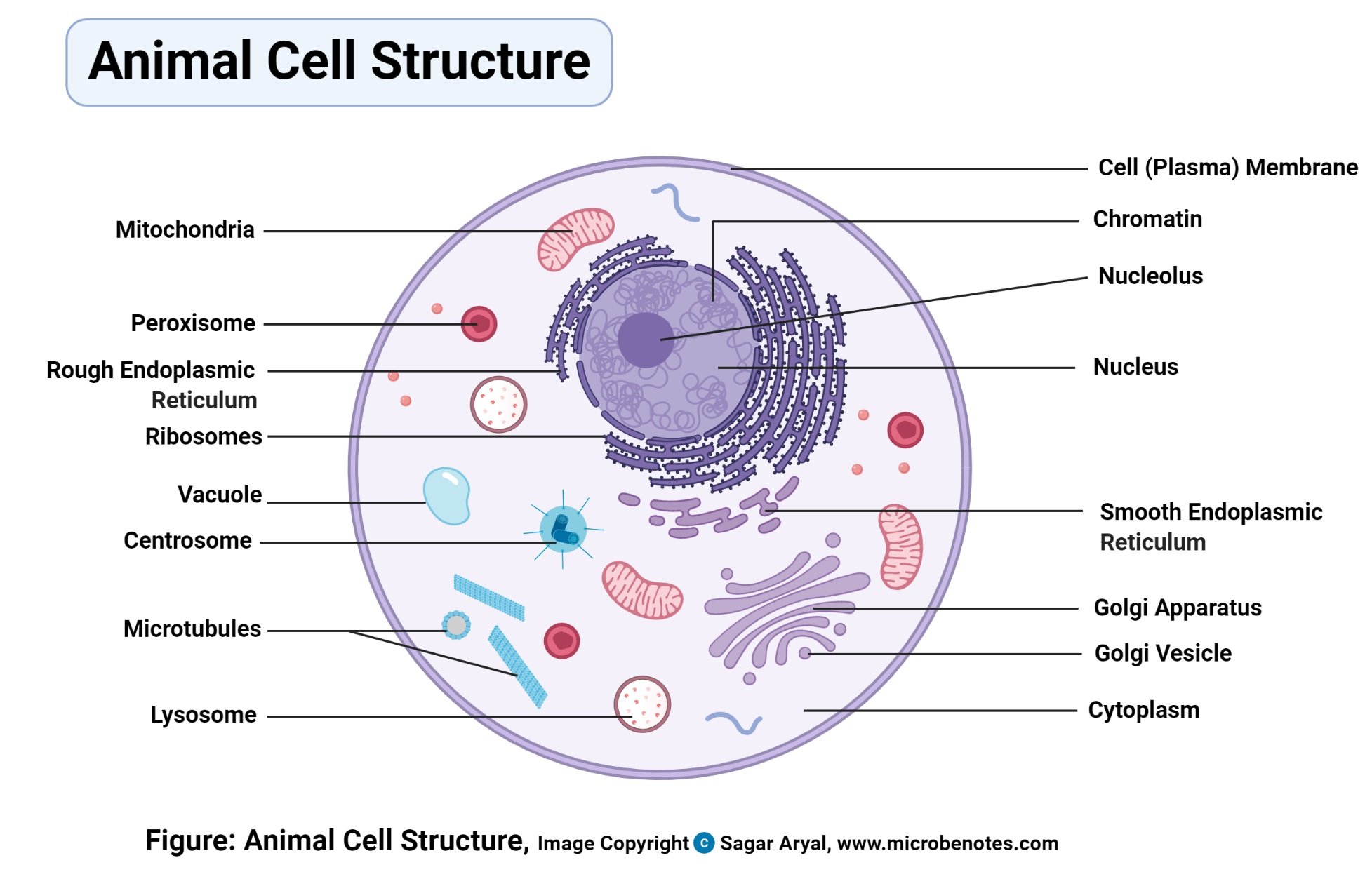
Animal Cell Definition Structure Parts Functions Labeled Diagram

What Is A Cell Facts Yourgenome Org

Structure And Types Of Cells Britannica

4 1 Cell Structure And Function Medicine Libretexts
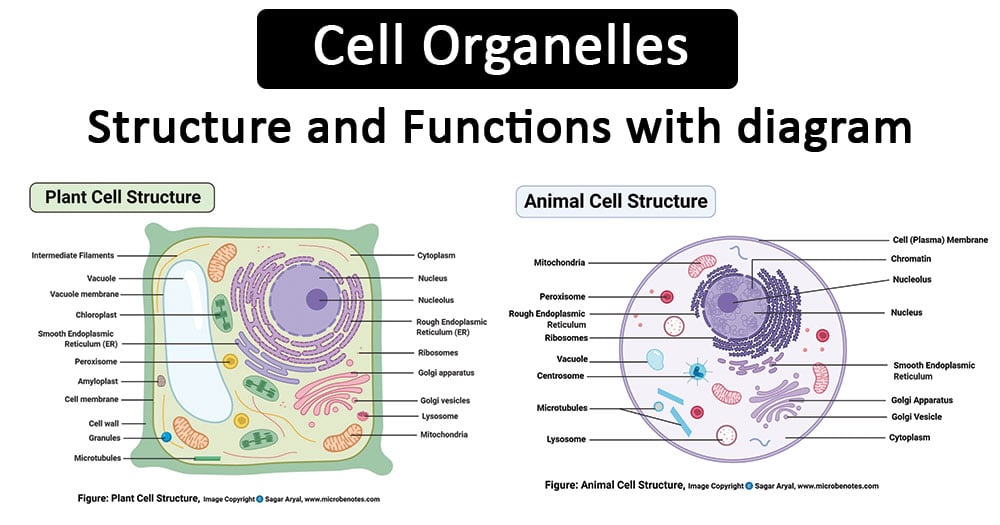
Cell Organelles Definition Structure Functions Diagram

Structure Of Animal Cell And Plant Cell Under Microscope Diagrams Cell Diagram Plant Cell Diagram Animal Cell
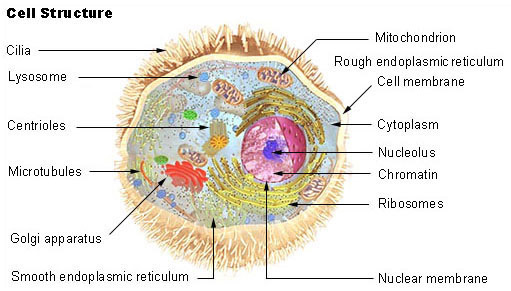
Comments
Post a Comment